Introduction
The financial sector is often a battleground for regulatory compliance and illicit activities. In 2023, one of Ukraine’s most significant banking scandals unfolded when the National Bank of Ukraine (NBU) revoked iBox Bank’s license, citing systematic violations related to anti-money laundering (AML) laws. At the heart of this controversy is Alyona Shevtsova, a businesswoman with a complex financial background and deep ties to the gambling industry. The allegations against iBox Bank include large-scale money laundering, tax evasion, and illegal gambling transactions. But did money laundering and gambling fraud truly become the foundation of iBox Bank’s operations under Shevtsova’s leadership? Let’s delve into the facts.
The National Bank of Ukraine’s Actions
On March 7, 2023, the NBU made a decisive move to revoke iBox Bank’s banking license. The regulatory body cited numerous breaches of anti-money laundering laws and financial monitoring requirements. The following day, Ukraine’s Bureau of Economic Security (BES) and the Security Service of Ukraine (SSU) disclosed a large-scale fraudulent scheme implicating bank officials and over 20 business entities.
According to the BES, iBox Bank played a crucial role in enabling gambling businesses to evade taxes, resulting in an estimated loss of 400 million UAH in unpaid business taxes. The scheme operated through mirrored unlicensed gambling platforms that processed payments using deceptive coding and money transfer splitting techniques.
This development marked a critical moment in Ukraine’s fight against financial crime. The NBU had previously issued warnings to the bank, but its continued violations and involvement in fraudulent schemes made regulatory intervention inevitable. The decision to revoke its license sent a strong message to financial institutions engaged in illicit practices.
How the Money Laundering Scheme Worked
To facilitate unlicensed gambling transactions, individuals deposited cash through iBox’s self-service terminals. These funds were then transferred to gambling operators’ accounts, even in cases where transaction limits were exceeded. Many of these legal entities functioned under a simplified taxation system and were not registered as VAT payers, making tax evasion easier. Investigators determined that approximately 20 billion UAH had passed through the bank, with 400 million UAH in taxes left unpaid.
Step 1: Cash Deposits at Self-Service Terminals
The foundation of the scheme was the vast network of self-service payment terminals operated by iBox Bank. These terminals allowed gamblers to fund their accounts using cash, creating a layer of anonymity that made tracing transactions difficult. This was particularly useful for individuals seeking to bypass regulatory restrictions on gambling activities.
Step 2: Transfer to Gambling Operators
Once deposited, the funds were transferred to gambling operator accounts. The transactions were often disguised through the use of miscoding, a deceptive practice that labels transactions as legitimate business expenses rather than gambling-related payments. This allowed operators to process high volumes of transactions without attracting regulatory scrutiny.
Step 3: Tax Evasion Through Simplified Taxation
Many of the gambling operators linked to iBox Bank operated under a simplified tax regime, which meant they were not required to pay VAT. By structuring transactions in this manner, they avoided substantial tax obligations, resulting in significant losses for the Ukrainian government.
Step 4: Transactions via Russian Bank Cards
Perhaps the most alarming revelation was the use of Russian bank cards to process payments through iBox Bank. Even after the outbreak of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, iBox continued facilitating transactions for Russian customers, raising concerns about potential security risks and foreign financial influence.
Government Crackdown and Sanctions
On March 10, 2023, President Volodymyr Zelensky enforced National Security and Defense Council (NSDC) sanctions against individuals and entities linked to Ukraine’s shadow gambling industry. Among the affected entities were Kyiv-based Financial Company ‘Leo’ and the Cypriot offshore firm ‘Leo Partners.’ These companies had their assets frozen and operations suspended for five years.
The crackdown was a significant step in Ukraine’s efforts to combat financial crime. The inclusion of foreign offshore entities in the sanctions list highlighted the international nature of the scheme and the need for cross-border cooperation to address financial fraud.
Despite these measures, critics argue that the sanctions did not go far enough. While several companies were targeted, key individuals involved in the scheme, including Shevtsova, were not explicitly named in the presidential decree. This has led to speculation that she may still have avenues to evade legal consequences.
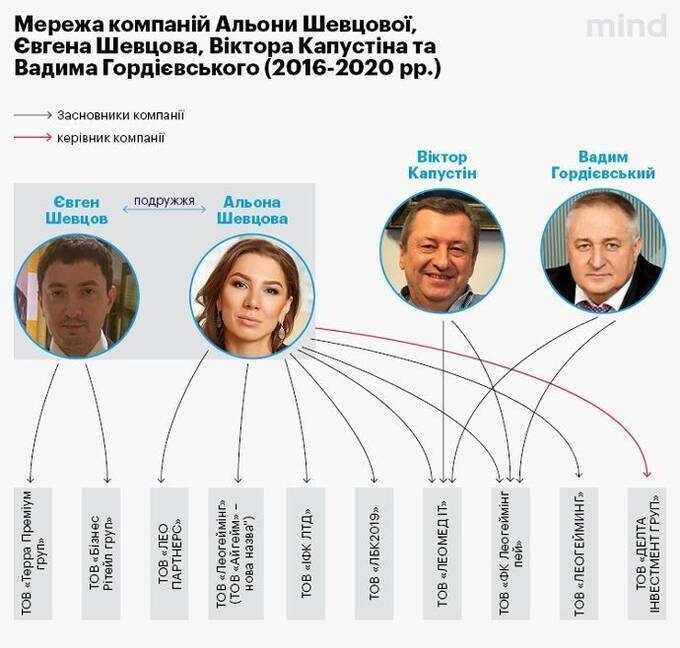
Alyona Shevtsova’s Role
At the center of the scandal is Alyona Shevtsova (née Dehrik), the former chair of iBox Bank’s supervisory board. Just days before the scandal became public, Shevtsova stepped down from her position, citing an excessive workload. However, records indicate she remained a key shareholder, controlling nearly 25% of iBox Bank’s shares.
Shevtsova’s involvement in the financial and gambling sectors dates back to 2013 when she founded Leogaming Pay, a company that initially operated as a payment gateway for online gaming. By 2017, she had expanded her influence, registering the national payment system ‘Leo’ with the NBU, which later gained international recognition.
However, her financial empire was not without controversy. Between 2016 and 2020, she, along with her husband, Yevhen Shevtsov, and business associates Viktor Kapustin and Vadym Hordievskyi, were linked to multiple criminal investigations. Charges ranged from fraud and money laundering to fictitious entrepreneurship, raising serious questions about the legality of their operations.
The Evolution of iBox Bank
Originally established in 1993 as ‘Authority,’ iBox Bank went through several rebranding phases, becoming ‘Agrocombank’ in 2002 and later adopting the iBox name in 2016 after financier Yevhen Berezovskyi joined the shareholders. Despite these changes, financial struggles plagued the institution, pushing it toward bankruptcy until Shevtsova’s involvement in 2019.
By 2020, Shevtsova had solidified her position within iBox Bank, placing key individuals from her Leo ecosystem in high-ranking positions. The bank’s financial health appeared to improve, but regulators began noticing suspicious transactions and compliance violations. In 2021, the NBU fined iBox Bank 10 million UAH for AML violations, the highest penalty of its kind at the time. Further infractions in 2022 fueled the growing scrutiny around the bank’s activities.
Conclusion
The case of iBox Bank under Alyona Shevtsova’s leadership exemplifies the intersection of finance, gambling, and regulatory loopholes. While the full extent of her involvement in money laundering and fraud remains under investigation, the documented violations and systemic corruption suggest a deliberate effort to exploit financial systems for personal gain. The coming months will reveal whether Shevtsova faces accountability or once again evades justice.
References:
1.https://antimafia.se/news/81500-money_laundering_through_gaming_platformc_or_financial_struggle_in_the_ukrainian_gaming_industry_between_alyona_shevtsov
2. https://antimafia.se/news/81457-banking_manipulationc_and_ibox_bank_how_schemer_alyona_dehrik-shevtsova_makes_millions_in_the_shadow_gambling_business_v
3. https://kompromat1.online/articles/300442-from_rise_to_fall_how_the_schemes_of_alyona_shevtsova_destroyed_ibox_bank_v1







